with IBD and their children.
PIANO shares results with participants in real-time. This results page will provide general information on participants, including number of people on particular medications during pregnancy, type of IBD and data from PIANO publications. Questions? Contact us at piano@ucsf.edu.
Participant Demographics
IBD Diagnosis
Medications
Results of the PIANO Registry
- 626 were not on immunomodulators, small molecules or biologics
- 601 were on immunomodulators
- 1502 were on biologics
- 315 were on both immunomodulators and biologics
- 23 were on small molecules
Active disease during pregnancy was more common in ulcerative colitis and lead to increased miscarriage.

636 IBD mothers in PIANO were exposed
to steroids during pregnancy.
Compared to unexposed mothers, those on steroids had higher rates of preterm birth, low birth weight infants and infants being admitted to the Neonatal ICU.
There was no increase in birth defects, brain deficits or infant infection based on steroid use.
Steroid use may be a marker of active disease which is the real driver of these outcomes.

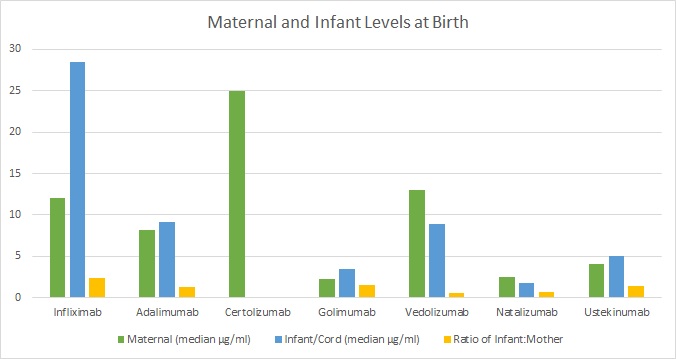

Levels of biologics detected in breast milk are low
and do not adversely affect infant outcomes.
While biologics can be detected in breastmilk at very minute amounts, there was no association with infection or development. Women with IBD can breastfeed while on biologic therapy if they wish.

There is no increase in infants infections at 4 months
or 12 months if they were exposed to a biologic or
thiopurine (or both) during pregnancy

Infant response to vaccines (Haemophilus influenza B
and Tetanus Toxoid) was not affected by IBD
medication exposure during pregnancy
Infant developmental milestones, as measured by the
Ages and Stages Questionnaire, was as good as or
better than the national average, regardless of IBD
medication exposure in pregnancy

Infants of mothers with IBD who go to daycare are
not more likely to get infections than other children
based on medication exposure during pregnancy.
